Anisotropic particles with tetrahedral symmetry: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Moved location of first reference) |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (→References: Added a recent publication) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b614955c Jonathan P. K. Doye, Ard A. Louis, I-Chun Lin, Lucy R. Allen, Eva G. Noya, Alex W. Wilber, Hoong Chwan Kok and Rosie Lyus "Controlling crystallization and its absence: proteins, colloids and patchy models", PCCP '''9''' pp. 2197-2205 (2007)] | *[http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b614955c Jonathan P. K. Doye, Ard A. Louis, I-Chun Lin, Lucy R. Allen, Eva G. Noya, Alex W. Wilber, Hoong Chwan Kok and Rosie Lyus "Controlling crystallization and its absence: proteins, colloids and patchy models", PCCP '''9''' pp. 2197-2205 (2007)] | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/32/322101 Flavio Romano, Piero Tartaglia and Francesco Sciortino "Gas–liquid phase coexistence in a tetrahedral patchy particle model", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter '''19''' 322101 (2007)] | *[http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/32/322101 Flavio Romano, Piero Tartaglia and Francesco Sciortino "Gas–liquid phase coexistence in a tetrahedral patchy particle model", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter '''19''' 322101 (2007)] | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3393777 Flavio Romano, Eduardo Sanz, and Francesco Sciortino "Phase diagram of a tetrahedral patchy particle model for different interaction ranges", Journal of Chemical Physics '''132''' 184501 (2010)] | |||
[[category: models]] | [[category: models]] | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 11 May 2010
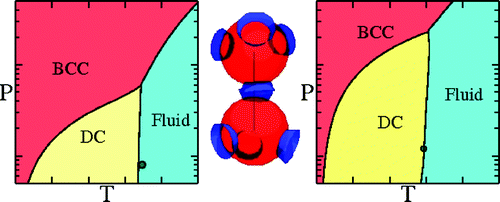
The phase diagram of the tetrahedral Kern and Frenkel patchy model exhibits the following solid phases[1]: diamond crystal (DC), body centred cubic (BCC) and face centred cubic (FCC). The gas-liquid critical point becomes metastable with respect to the diamond crystal when the range of the interaction becomes short (roughly less than 15% of the diameter).
In contrast to isotropic models, the critical point becomes only weakly metastable with respect to the solid as the interaction range
narrows (from left to right in the figure).
See also
References
Related reading
- Jiří Kolafa and Ivo Nezbeda "Monte Carlo simulations on primitive models of water and methanol", Molecular Physics 61 pp. 161-175 (1987)
- Jonathan P. K. Doye, Ard A. Louis, I-Chun Lin, Lucy R. Allen, Eva G. Noya, Alex W. Wilber, Hoong Chwan Kok and Rosie Lyus "Controlling crystallization and its absence: proteins, colloids and patchy models", PCCP 9 pp. 2197-2205 (2007)
- Flavio Romano, Piero Tartaglia and Francesco Sciortino "Gas–liquid phase coexistence in a tetrahedral patchy particle model", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 19 322101 (2007)
- Flavio Romano, Eduardo Sanz, and Francesco Sciortino "Phase diagram of a tetrahedral patchy particle model for different interaction ranges", Journal of Chemical Physics 132 184501 (2010)