Lennard-Jones model
The Lennard-Jones intermolecular pair potential is a special case of the Mie potential and takes its name from Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones [1] [2] The Lennard-Jones model consists of two 'parts'; a steep repulsive term, and smoother attractive term, representing the London dispersion forces. Apart from being an important model in its-self, the Lennard-Jones potential frequently forms one of 'building blocks' of may force fields,
Functional form
The Lennard-Jones potential is given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r) = 4 \epsilon \left[ \left(\frac{\sigma}{r} \right)^{12}- \left( \frac{\sigma}{r}\right)^6 \right] }
where
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r := |\mathbf{r}_1 - \mathbf{r}_2|}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r) } is the intermolecular pair potential between two particles or sites
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma } is the diameter (length), i.e. the value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} at which Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r)=0}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon } is the well depth (energy)
In reduced units:
- Density: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho^* := \rho \sigma^3 } , where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho := N/V } (number of particles Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N } divided by the volume Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V } )
- Temperature: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T^* := k_B T/\epsilon } , where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T } is the absolute temperature and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k_B } is the Boltzmann constant
The following is a plot of the Lennard-Jones model for the parameters Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon/k_B \approx} 120 K and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma \approx} 0.34 nm. See argon for different parameter sets.
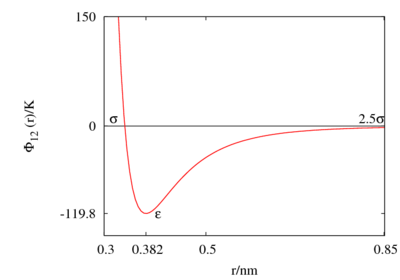
This figure was produced using gnuplot with the command:
plot (4*120*((0.34/x)**12-(0.34/x)**6))
Special points
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(\sigma) = 0 }
- Minimum value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r) } at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r = r_{min} } ;
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{r_{min}}{\sigma} = 2^{1/6} \simeq 1.12246 ... }
Critical point
The location of the critical point is [3]
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c^* = 1.326 \pm 0.002}
at a reduced density of
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho_c^* = 0.316 \pm 0.002} .
Vliegenthart and Lekkerkerker [4] have suggested that the critical point is related to the second virial coefficient via the expression
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_2 \vert_{T=T_c}= -\pi \sigma^3}
Triple point
The location of the triple point as found by Mastny and de Pablo (Ref. 4) is
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho_{tp}^* = 0.84} (liquid); Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho_{tp}^* = 0.96} (solid)
Approximations in simulation: truncation and shifting
The Lennard-Jones model is often used with a cutoff radius of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2.5 \sigma} , beyond which Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r)} is set to zero. See Mastny and de Pablo [5] for an analysis of the effect of this cutoff on the melting line.
n-m Lennard-Jones potential
It is relatively common to encounter potential functions given by:
with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m } being positive integers and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n > m } . Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c_{n,m} } is chosen such that the minimum value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r) } being Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{min} = - \epsilon } . Such forms are usually referred to as n-m Lennard-Jones Potential. For example, the 9-3 Lennard-Jones interaction potential is often used to model the interaction between the atoms/molecules of a fluid and a continuous solid wall. On the '9-3 Lennard-Jones potential' page a justification of this use is presented. Another example is the n-6 Lennard-Jones potential, where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m} is fixed at 6, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} is free to adopt a range of integer values. The potentials form part of the larger class of potentials known as the Mie potential.
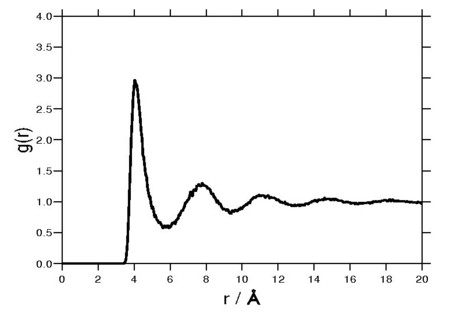
Radial distribution function
The following plot is of a typical radial distribution function for the monatomic Lennard-Jones liquid[6] (here with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma=3.73 {\mathrm {\AA}}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon=0.294} kcal/mol at a temperature of 111.06K):
Equation of state
- Main article: Lennard-Jones equation of state
Virial coefficients
- Main article: Lennard-Jones model: virial coefficients
Phase diagram
- Main article: Phase diagram of the Lennard-Jones model
Perturbation theory
The Lennard-Jones model is also used in perturbation theories, for example see: Weeks-Chandler-Anderson perturbation theory.
Mixtures
Related models
- 8-6 Lennard-Jones potential
- 9-3 Lennard-Jones potential
- 9-6 Lennard-Jones potential
- 10-4-3 Lennard-Jones potential
- n-6 Lennard-Jones potential
- Kihara potential
- Lennard-Jones model in 1-dimension (rods)
- Lennard-Jones model in 2-dimensions (disks)
- Lennard-Jones model in 4-dimensions
- Lennard-Jones sticks
- Mie potential
- Soft sphere potential
- Stockmayer potential
References
- ↑ John Edward Lennard-Jones "On the Determination of Molecular Fields. I. From the Variation of the Viscosity of a Gas with Temperature", Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character 106 pp. 441-462 (1924) § 8 (ii)
- ↑ John Edward Lennard-Jones "On the Determination of Molecular Fields. II. From the Equation of State of a Gas", Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character 106 pp. 463-477 (1924) Eq. 2.05
- ↑ J. M. Caillol " Critical-point of the Lennard-Jones fluid: A finite-size scaling study", Journal of Chemical Physics 109 pp. 4885-4893 (1998)
- ↑ G. A. Vliegenthart and H. N. W. Lekkerkerker "Predicting the gas–liquid critical point from the second virial coefficient", Journal of Chemical Physics 112 pp. 5364-5369 (2000)
- ↑ Ethan A. Mastny and Juan J. de Pablo "Melting line of the Lennard-Jones system, infinite size, and full potential", Journal of Chemical Physics 127 104504 (2007)
- ↑ John G. Kirkwood, Victor A. Lewinson, and Berni J. Alder "Radial Distribution Functions and the Equation of State of Fluids Composed of Molecules Interacting According to the Lennard-Jones Potential", Journal of Chemical Physics 20 pp. 929- (1952)

![{\displaystyle \Phi _{12}(r)=c_{n,m}\epsilon \left[\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{n}-\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{m}\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a7ef03a3a6ed92cc384a523b885962611ded7719)