Sutherland potential: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Added some more publications) |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Added plot of potential) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Sutherland potential''' <ref>W. Sutherland, Philosophical Magazine '''36''' pp. 507- (1893) </ref> is given by | [[Image:Sutherland.png|thumb|right]] | ||
The '''Sutherland potential''' <ref>W. Sutherland, Philosophical Magazine '''36''' pp. 507- (1893) </ref><ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.36.1025 H. W. Graben and R. D. Present "Third Virial Coefficient for the Sutherland (∞, ν) Potential", Reviews of Modern Physics '''36''' pp. 1025-1033 (1964)]</ref> is given by | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
'''Related reading''' | '''Related reading''' | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.431141 D. Levi and M. de Llano "Closed form of second virial coefficient for Sutherland potential", Journal of Chemical Physics '''63''' pp. 4561-4562 (1975)] | *[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.431141 D. Levi and M. de Llano "Closed form of second virial coefficient for Sutherland potential", Journal of Chemical Physics '''63''' pp. 4561-4562 (1975)] | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S0217979204025142 Jianxiang Tian and Yuanxing Gui "Liquid-gas phase transition to first order of an argon-like fluid modeled by the hard-core similar Sutherland potential", International Journal of Modern Physics B '''18''' pp. 2057-2069 (2004)] | *[http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S0217979204025142 Jianxiang Tian and Yuanxing Gui "Liquid-gas phase transition to first order of an argon-like fluid modeled by the hard-core similar Sutherland potential", International Journal of Modern Physics B '''18''' pp. 2057-2069 (2004)] | ||
Revision as of 13:49, 6 April 2010
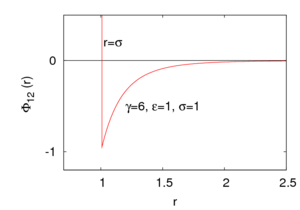
The Sutherland potential [1][2] is given by
where is the intermolecular pair potential, is the distance between site 1 and site 2, is the hard diameter, is the energy well depth (), and is a parameter that controls the interaction range.
References
- ↑ W. Sutherland, Philosophical Magazine 36 pp. 507- (1893)
- ↑ H. W. Graben and R. D. Present "Third Virial Coefficient for the Sutherland (∞, ν) Potential", Reviews of Modern Physics 36 pp. 1025-1033 (1964)
Related reading
- D. Levi and M. de Llano "Closed form of second virial coefficient for Sutherland potential", Journal of Chemical Physics 63 pp. 4561-4562 (1975)
- Jianxiang Tian and Yuanxing Gui "Liquid-gas phase transition to first order of an argon-like fluid modeled by the hard-core similar Sutherland potential", International Journal of Modern Physics B 18 pp. 2057-2069 (2004)
- A. Díez, J. Largo and J. R. Solana "Structure and thermodynamic properties of Sutherland fluids from computer simulation and the Tang–Lu integral equation theory", Fluid Phase Equilibria 253 pp. 67-73 (2007)
- Jianguo Mi, Yiping Tang, and Chongli Zhong "Theoretical study of Sutherland fluids with long-range, short-range, and highly short-range potential parameters", Journal of Chemical Physics 128 054503 (2008)
- Roman Melnyk, Pedro Orea, Ivo Nezbeda, and Andrij Trokhymchuk "Liquid/vapor coexistence and surface tension of the Sutherland fluid with a variable range of interaction: Computer simulation and perturbation theory studies", Journal of Chemical Physics 132 134504 (2010)
- F. Paragand, F. Feyzi and B. Behzadi "Application of the SAFT-VR equation of state to vapor–liquid equilibrium calculations for pure components and binary mixtures using the Sutherland potential", Fluid Phase Equilibria 290 pp. 181-194 (2010)






