SPC/E model of water: Difference between revisions
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Added a recent publication) |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Started a Thermal conductivity section) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| parameter || value | | parameter || value | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <math>\sigma</math> || <math> 3.166 | | <math>\sigma</math> || <math> 3.166 </math> Å | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <math>\epsilon</math> || <math>0.650</math> kJ mol<sup>-1</sup> | | <math>\epsilon</math> || <math>0.650</math> kJ mol<sup>-1</sup> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <math>r_\mathrm{OH}</math> || <math>1.000 | | <math>r_\mathrm{OH}</math> || <math>1.000</math> Å | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <math>\angle_\mathrm{HOH}</math> || <math>109.47^{\circ}</math> | | <math>\angle_\mathrm{HOH}</math> || <math>109.47^{\circ}</math> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
==Shear viscosity== | ==Shear viscosity== | ||
The [[shear viscosity]] for the SPC/E model is 0.729 mPa.s at 298 K and 1 bar <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3330544 Miguel Angel González and José L. F. Abascal "The shear viscosity of rigid water models", Journal of Chemical Physics '''132''' 096101 (2010)]</ref> (experimental value 0.896 mPa.s <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/je049918m Kenneth R. Harris and Lawrence A. Woolf "Temperature and Volume Dependence of the Viscosity of Water and Heavy Water at Low Temperatures", Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data '''49''' pp. 1064-1069 (2004)]</ref>). | The [[shear viscosity]] for the SPC/E model is 0.729 mPa.s at 298 K and 1 bar <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3330544 Miguel Angel González and José L. F. Abascal "The shear viscosity of rigid water models", Journal of Chemical Physics '''132''' 096101 (2010)]</ref> (experimental value 0.896 mPa.s <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/je049918m Kenneth R. Harris and Lawrence A. Woolf "Temperature and Volume Dependence of the Viscosity of Water and Heavy Water at Low Temperatures", Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data '''49''' pp. 1064-1069 (2004)]</ref>). | ||
==Thermal conductivity== | |||
[[Thermal conductivity]] <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4739855 Frank Römer, Anders Lervik, and Fernando Bresme "Nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulations of the thermal conductivity of water: A systematic investigation of the SPC/E and TIP4P/2005 models", Journal of Chemical Physics '''137''' 074503 (2012)]</ref>. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 19 September 2012
The SPC/E (extended simple point charge model) [1] [2] is a slight reparameterisation of the SPC model of water, with a modified value for . The molecule is modelled as a rigid isosceles triangle, having charges situated on each of the three atoms. Apart from Coulombic interactions, the molecules interact via long-range Lennard-Jones sites, situated on the oxygen atoms. The parameters are as follows:
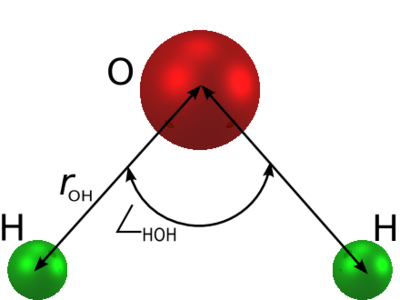
| parameter | value |
| Å | |
| kJ mol-1 | |
| Å | |
| (charge neutrality) |
The SPC/E model has a dipole moment of 2.351 D. (Ref. 1 Table I).
Surface tension
The surface tension has been studied for the SPC/E model by Vega and Miguel [3]
Phase diagram
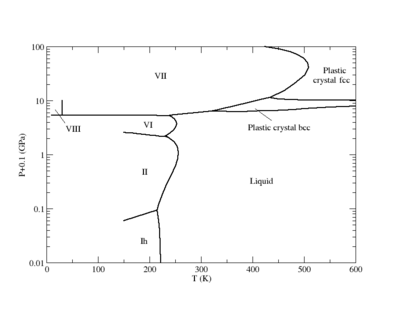
Plastic crystal phases
Recent simulations have demonstrated the existence of plastic crystal phases for the SPC/E model. [4]
Shear viscosity
The shear viscosity for the SPC/E model is 0.729 mPa.s at 298 K and 1 bar [5] (experimental value 0.896 mPa.s [6]).
Thermal conductivity
References
- ↑ H. J. C. Berendsen, J. R. Grigera, and T. P. Straatsma "The missing term in effective pair potentials", Journal of Physical Chemistry 91 pp. 6269 - 6271 (1987)
- ↑ Swaroop Chatterjee, Pablo G. Debenedetti, Frank H. Stillinger, and Ruth M. Lynden-Bell "A computational investigation of thermodynamics, structure, dynamics and solvation behavior in modified water models", Journal of Chemical Physics 128 124511 (2008)
- ↑ C. Vega and E. de Miguel "Surface tension of the most popular models of water by using the test-area simulation method", Journal of Chemical Physics 126 154707 (2007)
- ↑ J. L. Aragones and C. Vega "Plastic crystal phases of simple water models", Journal of Chemical Physics 130 244504 (2009)
- ↑ Miguel Angel González and José L. F. Abascal "The shear viscosity of rigid water models", Journal of Chemical Physics 132 096101 (2010)
- ↑ Kenneth R. Harris and Lawrence A. Woolf "Temperature and Volume Dependence of the Viscosity of Water and Heavy Water at Low Temperatures", Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 49 pp. 1064-1069 (2004)
- ↑ Frank Römer, Anders Lervik, and Fernando Bresme "Nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulations of the thermal conductivity of water: A systematic investigation of the SPC/E and TIP4P/2005 models", Journal of Chemical Physics 137 074503 (2012)
- Related reading











