Nematic phase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:nematic_ellipsoid.png|Nematic phase for the hard 6x1x1 ellipsoid model. |thumb|right]] | [[Image:nematic_ellipsoid.png|Nematic phase for the hard 6x1x1 ellipsoid model. |thumb|right]] | ||
The nematic phase has orientational order, but no positional order. | The nematic phase has orientational order, but no positional order. | ||
==Dielectric tensor== | |||
In the uniaxial nematic phase, defining the ''z''-axis to be parallel to the nematic axis, one has | |||
:<math>\epsilon_{\alpha \beta}= \begin{pmatrix} | |||
\epsilon_\bot & 0 & 0 \\ | |||
0 & \epsilon_\bot & 0 \\ | |||
0 & 0 & \epsilon_\| | |||
\end{pmatrix}</math> | |||
The anisotropy is defined as | |||
:<math>\Delta \epsilon = \epsilon_\| - \epsilon_\bot </math>. | |||
The response of a nematic liquid crystal | |||
to an external electric field depends on both the sign and the magnitude of <math>\Delta \epsilon</math>. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[category: liquid crystals]] | [[category: liquid crystals]] | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 23 July 2007
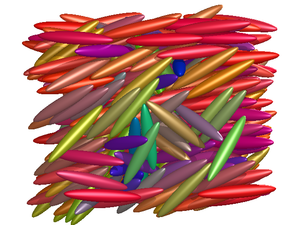
The nematic phase has orientational order, but no positional order.
Dielectric tensor
In the uniaxial nematic phase, defining the z-axis to be parallel to the nematic axis, one has
The anisotropy is defined as
- .
The response of a nematic liquid crystal to an external electric field depends on both the sign and the magnitude of .


