Lennard-Jones model: Difference between revisions
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Phase diagram of the Lennard-Jones model]] | *[[Phase diagram of the Lennard-Jones model]] | ||
*[[Lennard-Jones model: virial coefficients]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0959-5309/43/5/301 J. E. Lennard-Jones, "Cohesion", Proceedings of the Physical Society, '''43''' pp. 461-482 (1931)] | #[http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0959-5309/43/5/301 J. E. Lennard-Jones, "Cohesion", Proceedings of the Physical Society, '''43''' pp. 461-482 (1931)] | ||
[[Category:Models]] | [[Category:Models]] | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 16 August 2007
The Lennard-Jones potential was developed by Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones.
Lennard-Jones potential
The Lennard-Jones potential is given by:
where:
- is the intermolecular pair potential between two particles at a distance r;
- : diameter (length);
- : well depth (energy)
Reduced units:
- Density, , where (number of particles divided by the volume .)
- Temperature; , where is the absolute temperature and is the Boltzmann constant
Argon
The Lennard-Jones parameters for argon are 119.8 K and 0.3405 nm. (Ref. ?)
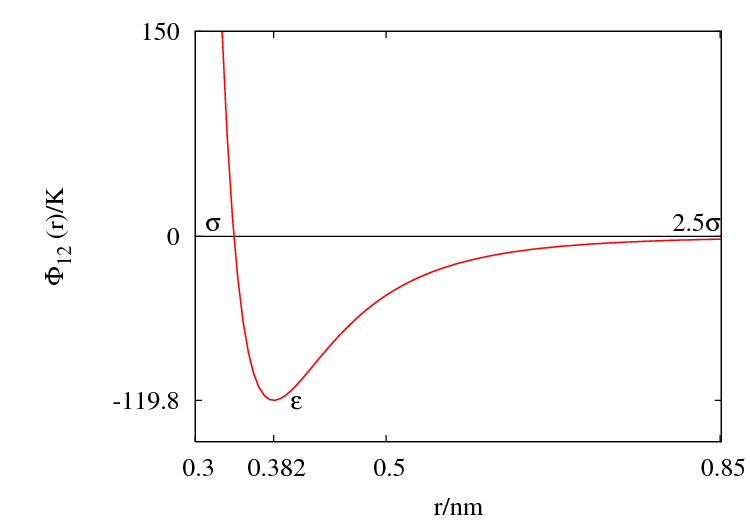
This figure was produced using gnuplot with the command:
plot (4*120*((0.34/x)**12-(0.34/x)**6))
Features
Special points:
- Minimum value of at ;
Approximations in simulation: truncation and shifting
Related potential models
It is relatively common the use of potential functions given by:
with and being positive integer numbers and , and is chosen to get the minimum value of being
These forms are usually referred to as m-n Lennard-Jones Potential.
The 9-3 Lennard-Jones interaction potential is often use to model the interaction between the atoms/molecules of a fluid and a continuous solid wall. In (9-3 Lennard-Jones potential) a justification of this use is presented.
Other dimensions
- 1-dimensional case: Lennard-Jones rods.
- 2-dimensional case: Lennard-Jones disks.
![{\displaystyle \Phi (r)=4\epsilon \left[\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{12}-\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{6}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b0ecd4ec335b5149b5f30ba2d02a6049d0407207)















![{\displaystyle \Phi (r)=c_{m,n}\epsilon \left[\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{m}-\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{n}\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/58317a77137d2a636f30e2a4a48c2ba87b516598)




