Nematic phase
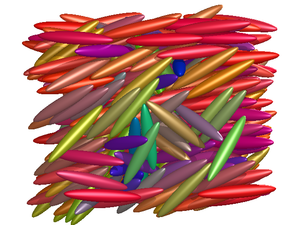
The nematic phase has orientational order, but no positional order.
Discotic nematic phase
Dielectric tensor
In the uniaxial nematic phase, defining the z-axis to be parallel to the nematic axis, one has
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_{\alpha \beta}= \begin{pmatrix} \epsilon_\bot & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \epsilon_\bot & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \epsilon_\| \end{pmatrix}}
The anisotropy is defined as
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta \epsilon = \epsilon_\| - \epsilon_\bot } .
The response of a nematic liquid crystal to an external electric field depends on both the sign and the magnitude of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta \epsilon} .
Biaxial nematic phase
- Jorge Peláez and Mark R. Wilson "Atomistic Simulations of a Thermotropic Biaxial Liquid Crystal", Physical Review Letters 97 267801 (2006)
- Carl McBride and Enrique Lomba "Hard biaxial ellipsoids revisited: Numerical results", Fluid Phase Equilibria 255 pp. 37-45 (2007)
- Roberto Berardi, Luca Muccioli, and Claudio Zannoni "Field response and switching times in biaxial nematics", Journal of Chemical Physics 128 024905 (2008)