Smectic phases: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) (Added a recent publication) |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Fixed typo) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:smectic_fused.png|Smectic phase of the fused hard sphere model. |thumb|right]] | [[Image:smectic_fused.png|Smectic phase of the fused hard sphere model. |thumb|right]] | ||
'''Smectic''' (from the Greek for soap <math>\sigma \mu \acute{\eta} \gamma \mu \alpha</math>). All of the smectic phases | |||
are layered, belonging to the <math>G_1^3</math> symmetry group. | are layered, belonging to the <math>G_1^3</math> symmetry group. | ||
==Smectic A phase== | ==Smectic A phase== | ||
Revision as of 15:28, 21 November 2013
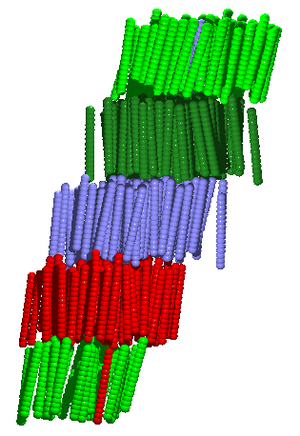
Smectic (from the Greek for soap ). All of the smectic phases are layered, belonging to the symmetry group.
Smectic A phase
In the smectic-A phase each layer is a 2-dimensional liquid, having the symmetry in the Schoenflies notation. [1] [2]
Smectic B phase
Smectic C phase
The smectic-C phase has the monoclinic symmetry .
Smectic E phase
Smectic F phase
References
- Related reading



