Smectic phases: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) (Added a recent publication) |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Added Latin) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:smectic_fused.png|Smectic phase of the fused hard sphere model. |thumb|right]] | [[Image:smectic_fused.png|Smectic phase of the fused hard sphere model. |thumb|right]] | ||
'''Smectic''' (from the Latin ''smecticus'' - "having the properties of soap" <ref>[http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/smectic Merriam-Webster]</ref>). All of the smectic phases | |||
are layered, belonging to the <math>G_1^3</math> symmetry group. | are layered, belonging to the <math>G_1^3</math> symmetry group. | ||
==Smectic A phase== | ==Smectic A phase== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:23, 5 March 2014
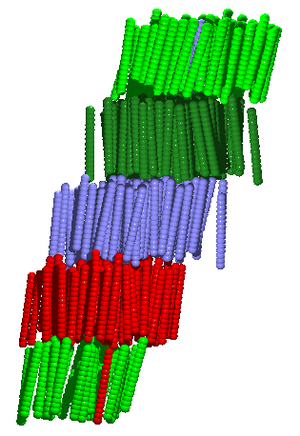
Smectic (from the Latin smecticus - "having the properties of soap" [1]). All of the smectic phases are layered, belonging to the symmetry group.
Smectic A phase[edit]
In the smectic-A phase each layer is a 2-dimensional liquid, having the symmetry in the Schoenflies notation. [2] [3]
Smectic B phase[edit]
Smectic C phase[edit]
The smectic-C phase has the monoclinic symmetry .
Smectic E phase[edit]
Smectic F phase[edit]
References[edit]
- Related reading


