Smectic phases: Difference between revisions
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
#[http://www.oup.com/us/catalog/general/subject/Physics/MaterialsScience/?view=usa&ci=9780198517856 Pierre-Gilles De Gennes and J. Prost "Physics of Liquid Crystals" (1995)] | #[http://www.oup.com/us/catalog/general/subject/Physics/MaterialsScience/?view=usa&ci=9780198517856 Pierre-Gilles De Gennes and J. Prost "Physics of Liquid Crystals" (1995)] | ||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cphc.200500472 Jan P. F. Lagerwall and Frank Giesselmann "Current Topics in Smectic Liquid Crystal Research", ChemPhysChem '''7''' pp. 20-45 (2006)] | |||
[[category: liquid crystals]] | [[category: liquid crystals]] | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 18 July 2007
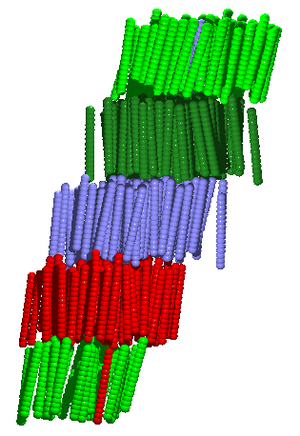
The work smectic comes from the Greek for soap (). All of the smectic phases are layered, belonging to the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_1^3} symmetry group.
Smectic A phase
In the smectic-A phase each layer is a 2-dimensional liquid, having the symmetry Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D_\infty} in the Schoenflies notation.
Smectic B phase
Smectic C phase
The smectic-C phase has the monoclinic symmetry Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_{\rm 2h}} .
