Lennard-Jones model: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | == Lennard-Jones potential == | ||
The '''Lennard-Jones''' potential is given by | The '''Lennard-Jones''' potential is given by | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* Temperature; <math> T^* \equiv k_B T/\epsilon </math>, where <math> T </math> is the absolute temperature and <math> k_B </math> is the [[Boltzmann constant]] | * Temperature; <math> T^* \equiv k_B T/\epsilon </math>, where <math> T </math> is the absolute temperature and <math> k_B </math> is the [[Boltzmann constant]] | ||
==Argon== | ==Argon== | ||
The Lennard-Jones parameters for argon are <math>\epsilon/k_B \approx</math> 119.8 K and <math>\sigma \approx</math> 0.3405 nm. (Ref. ?) | The Lennard-Jones parameters for argon are <math>\epsilon/k_B \approx</math> 119.8 K and <math>\sigma \approx</math> 0.3405 nm. (Ref. ?) | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 23 March 2007
Lennard-Jones potential
The Lennard-Jones potential is given by
where:
- : potential energy of interaction between two particles at a distance r;
- : diameter (length);
- : well depth (energy)
Reduced units:
- Density, , where (number of particles divided by the volume .)
- Temperature; , where is the absolute temperature and is the Boltzmann constant
Argon
The Lennard-Jones parameters for argon are 119.8 K and 0.3405 nm. (Ref. ?)
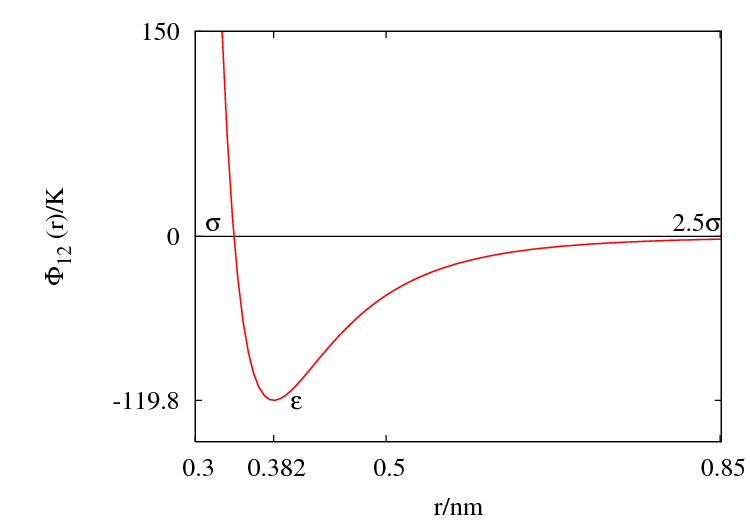
This figure was produced using gnuplot with the command:
plot (4*120*((0.34/x)**12-(0.34/x)**6))
Features
Special points:
- Minimum value of at ;
![{\displaystyle V(r)=4\epsilon \left[\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{12}-\left({\frac {\sigma }{r}}\right)^{6}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5256ed833acfbaa9f624a55f4be3f9fcb3c27e1a)














