Ramp model: Difference between revisions
m (→Lattice Gas Repulsive Ramp: small corrections) |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
This solid phase presents re-entrant melting, i.e. this solid melts into the fluid phase as the pressure is increased. | This solid phase presents re-entrant melting, i.e. this solid melts into the fluid phase as the pressure is increased. | ||
=== Lattice Gas | === Repulsive Ramp Lattice Gas Model === | ||
Recently, similar behaviour has been found in a three-dimensional [[lattice gas| | Recently, similar behaviour has been found in a three-dimensional Repulsive | ||
Ramp [[lattice gas|Lattice Gas]] model | |||
<ref> | <ref> | ||
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00268970902729269 Johan Skule Hoye, Enrique Lomba, and Noe Garcia Almarza, "One- and three-dimensional lattice models with two repulsive ranges: simple systems with complex phase behaviour", Molecular Physics ''iFirst'' (2009)] | [http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00268970902729269 Johan Skule Hoye, Enrique Lomba, and Noe Garcia Almarza, "One- and three-dimensional lattice models with two repulsive ranges: simple systems with complex phase behaviour", Molecular Physics ''iFirst'' (2009)] | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 6 March 2009
The ramp model, proposed by Jagla [1] and sometimes known as the Jagla model, is described by:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \infty & {\rm if} \; r < \sigma \\ W_r - (W_r-W_a) \frac{r-\sigma}{d_a-\sigma} & {\rm if} \; \sigma \leq r \leq d_a \\ W_a - W_a \frac{r-d_a}{d_c-d_a} & {\rm if} \; d_a < r \leq d_c \\ 0 & {\rm if} \; r > d_c \end{array} \right. }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{12}(r)} is the intermolecular pair potential, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r := |\mathbf{r}_1 - \mathbf{r}_2|} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle W_r > 0} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle W_a < 0} .
Graphically, one has:
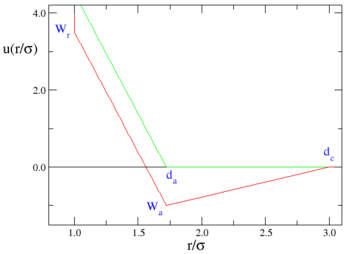
where the red line represents an attractive implementation of the model, and the green line a repulsive implementation.
Critical points
For the particular case Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle W_r^*=3.5; W_a^*=-1.0, d_a^*=1.72, d_c^*=3.0 } , the liquid-vapour critical point is located at [2]:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho_c \sigma^3 = 0.103 \pm 0.001}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_c^* \simeq 0.042}
and the liquid-liquid critical point:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c^* \simeq 0.378 \pm 0.003}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho_c \sigma^3 \simeq 0.380 \pm 0.002}
Repulsive Ramp Model
In the repulsive ramp case, where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle W_a = 0 } , neither liquid-vapor nor liquid-liquid stable equilibria occur [2]. However, for this model a low density crystalline phase has been found. This solid phase presents re-entrant melting, i.e. this solid melts into the fluid phase as the pressure is increased.
Repulsive Ramp Lattice Gas Model
Recently, similar behaviour has been found in a three-dimensional Repulsive Ramp Lattice Gas model [3]
The system is defined on a simple cubic lattice. The interaction is that of a Lattice hard sphere model with exclusion of nearest neighbors of occupied positions plus a repulsive interaction with next-to-nearest neighbors.
The potential energy of the system is then given by:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U = \epsilon \sum_{[ij]} S_i S_j }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon > 0 } ; Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [ij] } refers to all the pairs of sites that are second neighbors, and indicates the occupation of site Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k } (0 indicates empty site, 1 indicates occupied site).
See also
References
- ↑ E. A. Jagla "Core-softened potentials and the anomalous properties of water", Journal of Chemical Physics' 111 pp. 8980-8986 (1999)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1
E. Lomba, N. G. Almarza, C. Martin, C. McBride "Phase behaviour of attractive and repulsive ramp fluids: integral equation and computer simulation studies", Journal of Chemical Physics 126 244510 (2007)
Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "lomba" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Johan Skule Hoye, Enrique Lomba, and Noe Garcia Almarza, "One- and three-dimensional lattice models with two repulsive ranges: simple systems with complex phase behaviour", Molecular Physics iFirst (2009)
Related literature
- Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "Thermodynamics and dynamics of the two-scale spherically symmetric Jagla ramp model of anomalous liquids", Physical Review E 74 031108 (2006)
- Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Nicolas Giovambattista, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "A monatomic system with a liquid-liquid critical point and two distinct glassy states", Journal of Chemical Physics 130 054505 (2009)


