Ramp model: Difference between revisions
m (→Critical points: Added an internal link.) |
m (repulsive ramp model entry) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
:<math>\rho_c \sigma^3 \simeq 0.380 \pm 0.002</math> | :<math>\rho_c \sigma^3 \simeq 0.380 \pm 0.002</math> | ||
:<math>p_c^*/T_c^* \simeq 0.49 \pm 0.01</math> | :<math>p_c^*/T_c^* \simeq 0.49 \pm 0.01</math> | ||
== Repulsive Ramp Model == | |||
In the repulsive ramp case: <math> W_a = 0 </math>; neither liquid-vapor nor liquid-liquid stable equilibria occur | |||
(See Lomba et al. at the list of the references). However, for this model, it has been found a low density crystalline phase, | |||
This solid phase presents reentrant melting, i.e. It melts into the fluid phase at high pressure. | |||
Recently, the same behavior has ben found in a three-dimensional [[lattice gas|lattice gas]] ramp model <ref> | |||
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00268970902729269 Johan Skule Hoye, Enrique Lomba, and Noe Garcia Almarza, ''One- and three-dimensional lattice models with two repulsive ranges: simple systems with complex phase behaviour'' Mol. Phys 2009 ] </ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 20:25, 4 March 2009
The ramp model, proposed by Jagla [1] and sometimes known as the Jagla model, is described by:
where is the intermolecular pair potential, , and .
Graphically, one has:
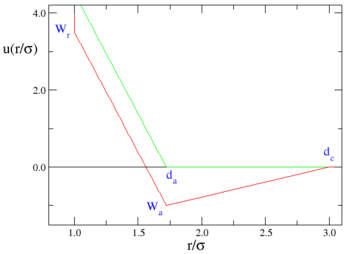
where the red line represents an attractive implementation of the model, and the green line a repulsive implementation.
Critical points
For the particular case , the liquid-vapour critical point is located at [2]:
and the liquid-liquid critical point:
Repulsive Ramp Model
In the repulsive ramp case: ; neither liquid-vapor nor liquid-liquid stable equilibria occur (See Lomba et al. at the list of the references). However, for this model, it has been found a low density crystalline phase, This solid phase presents reentrant melting, i.e. It melts into the fluid phase at high pressure.
Recently, the same behavior has ben found in a three-dimensional lattice gas ramp model [3]
See also
References
- ↑ E. A. Jagla "Core-softened potentials and the anomalous properties of water", Journal of Chemical Physics' 111 pp. 8980-8986 (1999)
- ↑ E. Lomba, N. G. Almarza, C. Martin, C. McBride "Phase behaviour of attractive and repulsive ramp fluids: integral equation and computer simulation studies", Journal of Chemical Physics 126 244510 (2007)
- ↑ Johan Skule Hoye, Enrique Lomba, and Noe Garcia Almarza, One- and three-dimensional lattice models with two repulsive ranges: simple systems with complex phase behaviour Mol. Phys 2009
Related literature
- Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "Thermodynamics and dynamics of the two-scale spherically symmetric Jagla ramp model of anomalous liquids", Physical Review E 74 031108 (2006)
- Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Nicolas Giovambattista, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "A monatomic system with a liquid-liquid critical point and two distinct glassy states", Journal of Chemical Physics 130 054505 (2009)












