Ramp model: Difference between revisions
m (Internal link added) |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (→References: Added a recent publication) |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.74.031108 Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "Thermodynamics and dynamics of the two-scale spherically symmetric Jagla ramp model of anomalous liquids", Physical Review E '''74''' 031108 (2006)] | *[http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.74.031108 Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "Thermodynamics and dynamics of the two-scale spherically symmetric Jagla ramp model of anomalous liquids", Physical Review E '''74''' 031108 (2006)] | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3043665 Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Nicolas Giovambattista, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "A monatomic system with a liquid-liquid critical point and two distinct glassy states", Journal of Chemical Physics '''130''' 054505 (2009)] | *[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3043665 Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Nicolas Giovambattista, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "A monatomic system with a liquid-liquid critical point and two distinct glassy states", Journal of Chemical Physics '''130''' 054505 (2009)] | ||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms11125184 Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Nicolas Giovambattista, and H. Eugene Stanley "Liquid-Liquid Phase Transition and Glass Transition in a Monoatomic Model", International Journal of Molecular Sciences '''11''' pp. 5184-5200 (2010)] | |||
[[Category:models]] | [[Category:models]] | ||
[[category:Polyamorphic systems]] | [[category:Polyamorphic systems]] | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 4 February 2011
The ramp model, proposed by Jagla [1] and sometimes known as the Jagla model, is described by:
where is the intermolecular pair potential, , and .
Graphically, one has:
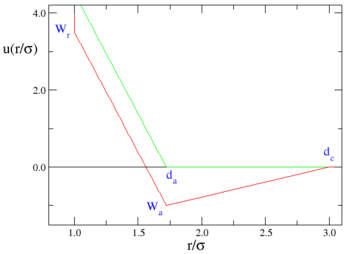
where the red line represents an attractive implementation of the model, and the green line a repulsive implementation.
Critical points
For the particular case , the liquid-vapour critical point is located at [2]:
and the liquid-liquid critical point:
Repulsive Ramp Model
In the repulsive ramp case, where , neither liquid-vapor nor liquid-liquid stable equilibria occur [2]. However, for this model a low density crystalline phase has been found. This solid phase presents re-entrant melting, i.e. this solid melts into the fluid phase as the pressure is increased.
Lattice gas version
Recently, similar behaviour has been found in a three-dimensional Repulsive Ramp Lattice Gas model [3] The system is defined on a simple cubic lattice. The interaction is that of a lattice hard sphere model with exclusion of nearest neighbours of occupied positions plus a repulsive interaction with next-to-nearest neighbours. The total potential energy of the system is then given by:
where ; refers to all the pairs of sites that are second neighbors, and indicates the occupation of site (0 indicates an empty site, 1 indicates an occupied site).
See also
References
- ↑ E. A. Jagla "Core-softened potentials and the anomalous properties of water", Journal of Chemical Physics' 111 pp. 8980-8986 (1999)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1
E. Lomba, N. G. Almarza, C. Martin, C. McBride "Phase behaviour of attractive and repulsive ramp fluids: integral equation and computer simulation studies", Journal of Chemical Physics 126 244510 (2007)
Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "lomba" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Johan Skule Hoye, Enrique Lomba, and Noe Garcia Almarza, "One- and three-dimensional lattice models with two repulsive ranges: simple systems with complex phase behaviour", Molecular Physics 107, 321-330 (2009)
Related literature
- Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "Thermodynamics and dynamics of the two-scale spherically symmetric Jagla ramp model of anomalous liquids", Physical Review E 74 031108 (2006)
- Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Nicolas Giovambattista, C. Austen Angell, and H. Eugene Stanley "A monatomic system with a liquid-liquid critical point and two distinct glassy states", Journal of Chemical Physics 130 054505 (2009)
- Limei Xu, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Nicolas Giovambattista, and H. Eugene Stanley "Liquid-Liquid Phase Transition and Glass Transition in a Monoatomic Model", International Journal of Molecular Sciences 11 pp. 5184-5200 (2010)













![{\displaystyle U=\epsilon \sum _{[ij]}S_{i}S_{j}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/47128ac7d19cf407aa50871277c85fc5139db8d1)

![{\displaystyle [ij]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4d30520e09683aad1e38713ce1a8182cde93c0ce)

