Hard superball model
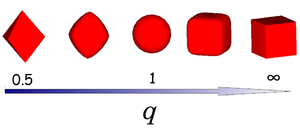
A superball is defined by the inequality
where x, y and z are scaled Cartesian coordinates with q the deformation parameter and radius a. The shape of the superball interpolates smoothly between two Platonic solids, namely the octahedron (q = 0.5) and the cube (q = ∞) via the sphere (q = 1) as shown in the left figure.
