Hard superball model: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Fixed volume equation formatting) |
(simplified definition of superball and volume formula) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The '''hard superball model''' is defined by the inequality | The '''hard superball model''' is defined by the inequality | ||
:<math> | :<math>|x|^{2q} + |y|^{2q} +|z|^{2q} \le a^{2q}</math> | ||
where ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'' are scaled Cartesian coordinates with ''q'' the deformation parameter and radius ''a''. The shape of the superball interpolates smoothly between two Platonic solids, namely the octahedron (''q'' = 0.5) and the [[Hard cube model |cube]] (''q'' = ∞) via the [[Hard sphere model |sphere]] (''q'' = 1) as shown in the right figure. | where ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'' are scaled Cartesian coordinates with ''q'' the deformation parameter and radius ''a''. The shape of the superball interpolates smoothly between two Platonic solids, namely the octahedron (''q'' = 0.5) and the [[Hard cube model |cube]] (''q'' = ∞) via the [[Hard sphere model |sphere]] (''q'' = 1) as shown in the right figure. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
v(q,a) & = & 8 a^3 \int_{0}^1 \int_{0}^{(1-x^{2q})^{1/2q}} (1-x^{2q}-y^{2q})^{1/2q} \mathrm{d}\, y \, \mathrm{d}\, x \\ | v(q,a) & = & 8 a^3 \int_{0}^1 \int_{0}^{(1-x^{2q})^{1/2q}} (1-x^{2q}-y^{2q})^{1/2q} \mathrm{d}\, y \, \mathrm{d}\, x \\ | ||
& = & \frac{ | & = & \frac{2a^3\left[ \Gamma\left(1+1/2q\right) \right]^3}{3q^2\Gamma\left(1+ 3/2q\right)}, | ||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
Revision as of 23:53, 2 April 2018
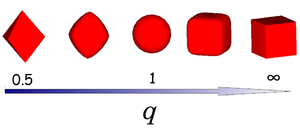
The hard superball model is defined by the inequality
where x, y and z are scaled Cartesian coordinates with q the deformation parameter and radius a. The shape of the superball interpolates smoothly between two Platonic solids, namely the octahedron (q = 0.5) and the cube (q = ∞) via the sphere (q = 1) as shown in the right figure.
Particle Volume
The volume of a superball with the shape parameter q and radius a is given by
where is the Gamma function.
Overlap algorithm
The most widely used overlap algorithm is on the basis of Perram and Wertheim method [1] [2].
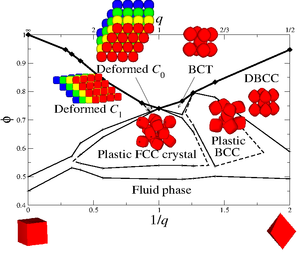
Phase diagram
The full phase diagram of hard superballs whose shape interpolates from cubes to octahedra was reported in Ref [2].
References
- ↑ John W. Perram and M. S. Wertheim "Statistical mechanics of hard ellipsoids. I. Overlap algorithm and the contact function", Journal of Computational Physics 58 pp. 409-416 (1985)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 R. Ni, A.P. Gantapara, J. de Graaf, R. van Roij, and M. Dijkstra "Phase diagram of colloidal hard superballs: from cubes via spheres to octahedra", Soft Matter 8 pp. 8826-8834 (2012)


![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}v(q,a)&=&8a^{3}\int _{0}^{1}\int _{0}^{(1-x^{2q})^{1/2q}}(1-x^{2q}-y^{2q})^{1/2q}\mathrm {d} \,y\,\mathrm {d} \,x\\&=&{\frac {2a^{3}\left[\Gamma \left(1+1/2q\right)\right]^{3}}{3q^{2}\Gamma \left(1+3/2q\right)}},\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a0a591f0e20c2655b8a1495e62fbee948dc652f7)
