Hard spherocylinders: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Added short section on the minimum distance.) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
where <math>L</math> is the length of the cylindrical part of the spherocylinder and <math>D</math> is the diameter. | where <math>L</math> is the length of the cylindrical part of the spherocylinder and <math>D</math> is the diameter. | ||
==Minimum distance== | |||
The minimum distance between two spherocylinders can be calculated using an algorithm published by Vega and Lago (Ref. 1). The [[Source code for the minimum distance between two rods | source code can be found here]]. Such an algorithm is essential in, for example, a [[Monte Carlo]] simulation, in order to check for overlaps between two sites. | |||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0097-8485(94)80023-5 Carlos Vega and Santiago Lago "A fast algorithm to evaluate the shortest distance between rods", Computers & Chemistry '''18''' pp. 55-59 (1994)] | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Charged hard spherocylinders]] | *[[Charged hard spherocylinders]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.471343 S. C. McGrother and D. C. Williamson and G. Jackson "A re-examination of the phase diagram of hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics '''104''' pp. 6755-6771 (1996)] | |||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.473404 P. Bolhuis and D. Frenkel "Tracing the phase boundaries of hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics '''106''' pp. 666-687 (1997)] | |||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2207141 Giorgio Cinacchi and Yuri Martínez-Ratón and Luis Mederos and Enrique Velasco "Smectic, nematic, and isotropic phases in binary mixtures of thin and thick hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics '''124''' pp. 234904 (2006)] | #[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2207141 Giorgio Cinacchi and Yuri Martínez-Ratón and Luis Mederos and Enrique Velasco "Smectic, nematic, and isotropic phases in binary mixtures of thin and thick hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics '''124''' pp. 234904 (2006)] | ||
[[Category: Models]] | [[Category: Models]] | ||
Revision as of 11:38, 23 July 2008
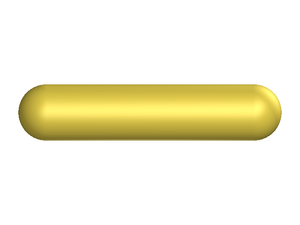
The hard spherocylinder model consists on an impenetrable cylinder, capped at both ends by hemispheres whose diameters are the same as the diameter of the cylinder. The molecular volume of the spherocylinder is given by
where is the length of the cylindrical part of the spherocylinder and is the diameter.
Minimum distance
The minimum distance between two spherocylinders can be calculated using an algorithm published by Vega and Lago (Ref. 1). The source code can be found here. Such an algorithm is essential in, for example, a Monte Carlo simulation, in order to check for overlaps between two sites.
See also
References
- S. C. McGrother and D. C. Williamson and G. Jackson "A re-examination of the phase diagram of hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics 104 pp. 6755-6771 (1996)
- P. Bolhuis and D. Frenkel "Tracing the phase boundaries of hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics 106 pp. 666-687 (1997)
- Giorgio Cinacchi and Yuri Martínez-Ratón and Luis Mederos and Enrique Velasco "Smectic, nematic, and isotropic phases in binary mixtures of thin and thick hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics 124 pp. 234904 (2006)


