Hard spherocylinders: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
where <math>L</math> is the length of the cylindrical part of the spherocylinder and <math>D</math> is the diameter. | where <math>L</math> is the length of the cylindrical part of the spherocylinder and <math>D</math> is the diameter. | ||
==See also== | |||
*[[Charged hard spherocylinders]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
#[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2207141 Giorgio Cinacchi and Yuri Martínez-Ratón and Luis Mederos and Enrique Velasco "Smectic, nematic, and isotropic phases in binary mixtures of thin and thick hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics '''124''' pp. 234904 (2006)] | #[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2207141 Giorgio Cinacchi and Yuri Martínez-Ratón and Luis Mederos and Enrique Velasco "Smectic, nematic, and isotropic phases in binary mixtures of thin and thick hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics '''124''' pp. 234904 (2006)] | ||
Revision as of 14:26, 1 February 2008
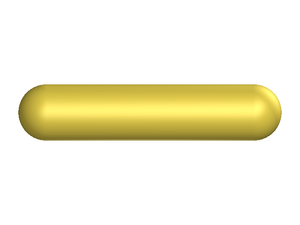
The molecular volume of the spherocylinder is given by
where is the length of the cylindrical part of the spherocylinder and is the diameter.
See also
References
- Giorgio Cinacchi and Yuri Martínez-Ratón and Luis Mederos and Enrique Velasco "Smectic, nematic, and isotropic phases in binary mixtures of thin and thick hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics 124 pp. 234904 (2006)
- P. Bolhuis and D. Frenkel "Tracing the phase boundaries of hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics 106 pp. 666-687 (1997)
- S. C. McGrother and D. C. Williamson and G. Jackson "A re-examination of the phase diagram of hard spherocylinders", Journal of Chemical Physics 104 pp. 6755-6771 (1996)


