Anisotropic particles with tetrahedral symmetry: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
m (Slight tidy.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
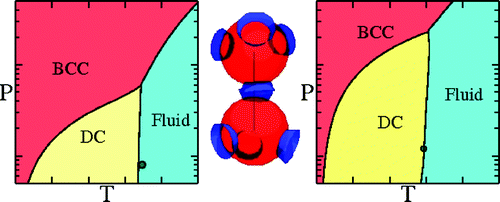
The phase diagram of tetrahedral | The '''phase diagram of tetrahedral''' [[patchy particles]] <ref>[http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp9081905 F. Romano, E. Sanz and F. Sciortino "Role of the Range in the Fluid−Crystal Coexistence for a Patchy Particle Model", Journal of Physical Chemistry B '''113''' pp. 15133–15136 (2009)]</ref> | ||
Patchy Particle Model", | exhibits the following solid phases: [[Building up a diamond lattice |diamond crystal]] (DC), | ||
exhibits the following solid phases: | [[Building up a body centered cubic lattice | body centred cubic]] (BCC) and [[Building up a face centered cubic lattice |face centred cubic]] (FCC). The gas-liquid [[critical points | critical point]] becomes metastable with respect | ||
to the diamond crystal when the range of the interaction becomes short (roughly less than 15% of the | |||
to the | |||
diameter). | diameter). | ||
:[[Image:romanojpcb09.gif]] | |||
In contrast to isotropic models, the critical point becomes only weakly metastable with respect to the solid as the interaction range | |||
narrows (from left to right in the figure). | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[category: models]] | |||
Revision as of 11:34, 30 November 2009
The phase diagram of tetrahedral patchy particles [1] exhibits the following solid phases: diamond crystal (DC), body centred cubic (BCC) and face centred cubic (FCC). The gas-liquid critical point becomes metastable with respect to the diamond crystal when the range of the interaction becomes short (roughly less than 15% of the diameter).
In contrast to isotropic models, the critical point becomes only weakly metastable with respect to the solid as the interaction range
narrows (from left to right in the figure).